React中Diff算法是什么?Diff算法的策略及完成
时间:2024/5/30作者:未知来源:争怎路由网人气:5
- 网页的本质就是超级文本标记语言,通过结合使用其他的Web技术(如:脚本语言、公共网关接口、组件等),可以创造出功能强大的网页。因而,超级文本标记语言是万维网(Web)编程的基础,也就是说万维网是建立在超文本基础之上的。超级文本标记语言之所以称为超文本标记语言,是因为文本中包含了所谓“超级链接”点。本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于React中Diff算法是什么?Diff算法的策略及实现,有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
1、什么是Diff算法
传统Diff:diff算法即差异查找算法;对于Html DOM结构即为tree的差异查找算法;而对于计算两颗树的差异时间复杂度为O(n^3),显然成本太高,React不可能采用这种传统算法;
React Diff:
之前说过,React采用虚拟DOM技术实现对真实DOM的映射,即React Diff算法的差异查找实质是对两个JavaScript对象的差异查找;
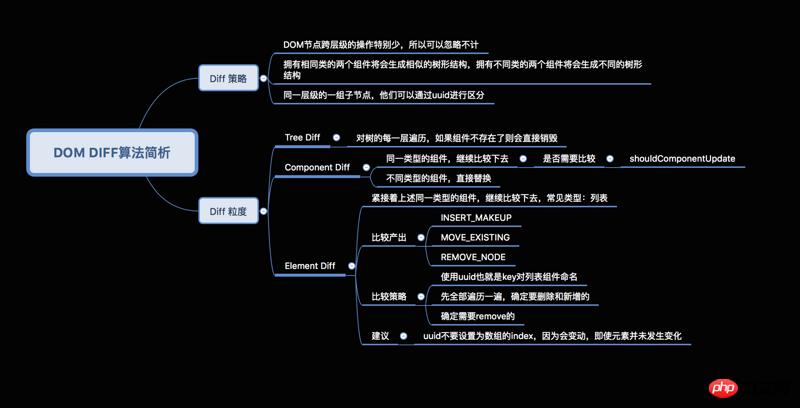
基于三个策略:
Web UI 中 DOM 节点跨层级的移动操作特别少,可以忽略不计。(tree diff)
拥有相同类的两个组件将会生成相似的树形结构,拥有不同类的两个组件将会生成不同的树形结(component diff)
对于同一层级的一组子节点,它们可以通过唯一 id 进行区分。(element diff)
2、React Diff算法解读
首先需要明确,只有在React更新阶段才会有Diff算法的运用;
React更新机制:
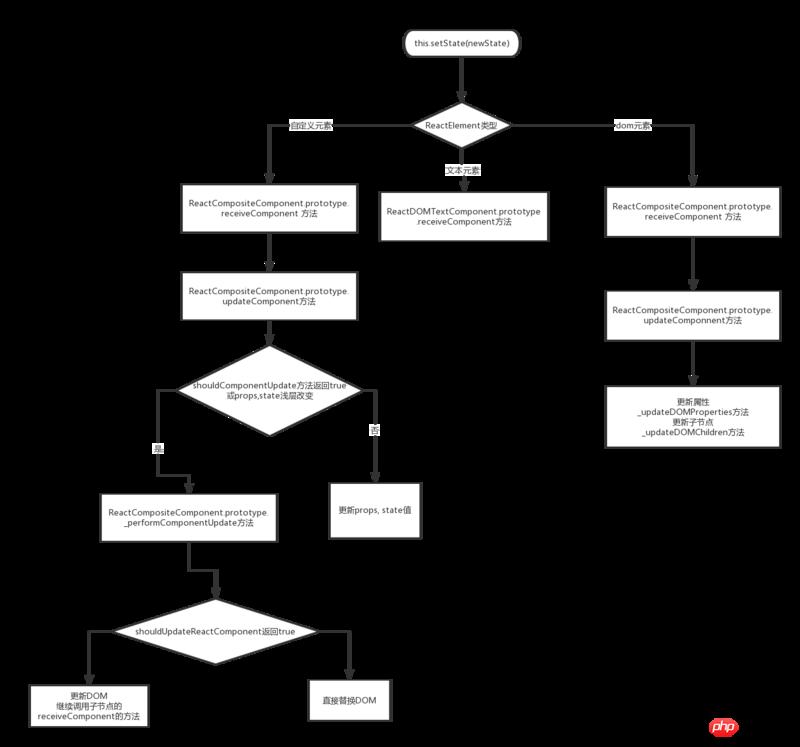
React Diff算法优化策略图:
React更新阶段会对ReactElement类型判断而进行不同的操作;ReactElement类型包含三种即:文本、Dom、组件;
每个类型的元素更新处理方式:
自定义元素的更新,主要是更新render出的节点,做甩手掌柜交给render出的节点的对应component去管理更新。
text节点的更新很简单,直接更新文案。
浏览器基本元素的更新,分为两块:
更新属性,对比出前后属性的不同,局部更新。并且处理特殊属性,比如事件绑定。
子节点的更新,子节点更新主要是找出差异对象,找差异对象的时候也会使用上面的shouldUpdateReactComponent来判断,如果是可以直接更新的就会递归调用子节点的更新,这样也会递归查找差异对象。不可直接更新的删除之前的对象或添加新的对象。之后根据差异对象操作dom元素(位置变动,删除,添加等)。
事实上Diff算法只被调用于React更新阶段的DOM元素更新过程;为什么这么说?
1、 如果为更新文本类型,内容不同就直接更新替换,并不会调用复杂的Diff算法:
ReactDOMTextComponent.prototype.receiveComponent(nextText, transaction) { //与之前保存的字符串比较 if (nextText !== this._currentElement) { this._currentElement = nextText; var nextStringText = '' + nextText; if (nextStringText !== this._stringText) { this._stringText = nextStringText; var commentNodes = this.getHostNode(); // 替换文本元素 DOMChildrenOperations.replaceDelimitedText( commentNodes[0], commentNodes[1], nextStringText ); } } }2、对于自定义组件元素:
class Tab extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { index: 1, } } shouldComponentUpdate() { .... } render() { return ( <p> <p>item1</p> <p>item1</p> </p> ) } }需要明确的是,何为组件,可以说组件只不过是一段Html结构的包装容器,并且具备管理这段Html结构的状态等能力;
如上述Tab组件:它的实质内容就是render函数返回的Html结构,而我们所说的Tab类就是这段Html结构的包装容器(可以理解为一个包装盒子);
在React渲染机制图中可以看到,自定义组件的最后结合React Diff优化策略一(不同类的两个组件具备不同的结构)
3、基本元素:
ReactDOMComponent.prototype.receiveComponent = function(nextElement, transaction, context) { var prevElement = this._currentElement; this._currentElement = nextElement; this.updateComponent(transaction, prevElement, nextElement, context); } ReactDOMComponent.prototype.updateComponent = function(transaction, prevElement, nextElement, context) { //需要单独的更新属性 this._updateDOMProperties(lastProps, nextProps, transaction, isCustomComponentTag); //再更新子节点 this._updateDOMChildren( lastProps, nextProps, transaction, context ); // ...... }在this._updateDOMChildren方法内部才调用了diff算法。
3、React中Diff算法的实现
_updateChildren: function(nextNestedChildrenElements, transaction, context) { var prevChildren = this._renderedChildren; var removedNodes = {}; var mountImages = []; // 获取新的子元素数组 var nextChildren = this._reconcilerUpdateChildren( prevChildren, nextNestedChildrenElements, mountImages, removedNodes, transaction, context ); if (!nextChildren && !prevChildren) { return; } var updates = null; var name; var nextIndex = 0; var lastIndex = 0; var nextMountIndex = 0; var lastPlacedNode = null; for (name in nextChildren) { if (!nextChildren.hasOwnProperty(name)) { continue; } var prevChild = prevChildren && prevChildren[name]; var nextChild = nextChildren[name]; if (prevChild === nextChild) { // 同一个引用,说明是使用的同一个component,所以我们需要做移动的操作 // 移动已有的子节点 // NOTICE:这里根据nextIndex, lastIndex决定是否移动 updates = enqueue( updates, this.moveChild(prevChild, lastPlacedNode, nextIndex, lastIndex) ); // 更新lastIndex lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex); // 更新component的.mountIndex属性 prevChild._mountIndex = nextIndex; } else { if (prevChild) { // 更新lastIndex lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex); } // 添加新的子节点在指定的位置上 updates = enqueue( updates, this._mountChildAtIndex( nextChild, mountImages[nextMountIndex], lastPlacedNode, nextIndex, transaction, context ) ); nextMountIndex++; } // 更新nextIndex nextIndex++; lastPlacedNode = ReactReconciler.getHostNode(nextChild); } // 移除掉不存在的旧子节点,和旧子节点和新子节点不同的旧子节点 for (name in removedNodes) { if (removedNodes.hasOwnProperty(name)) { updates = enqueue( updates, this._unmountChild(prevChildren[name], removedNodes[name]) ); } } }4、基于中Diff的开发建议
基于tree diff:
开发组件时,注意保持DOM结构的稳定;即,尽可能少地动态操作DOM结构,尤其是移动操作。
当节点数过大或者页面更新次数过多时,页面卡顿的现象会比较明显。
这时可以通过 CSS 隐藏或显示节点,而不是真的移除或添加 DOM 节点。
基于component diff:
注意使用 shouldComponentUpdate() 来减少组件不必要的更新。
对于类似的结构应该尽量封装成组件,既减少代码量,又能减少component diff的性能消耗。
基于element diff:
对于列表结构,尽量减少类似将最后一个节点移动到列表首部的操作,当节点数量过大或更新操作过于频繁时,在一定程度上会影响 React 的渲染性能。
以上就是React中Diff算法是什么?Diff算法的策略及实现的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
网站建设是一个广义的术语,涵盖了许多不同的技能和学科中所使用的生产和维护的网站。
关键词:React中Diff算法是啥?Diff算法的策略及完成