vue完成用户登录验证(vue完成登录注册与验证码)
时间:2024/11/13作者:未知来源:争怎路由网人气:
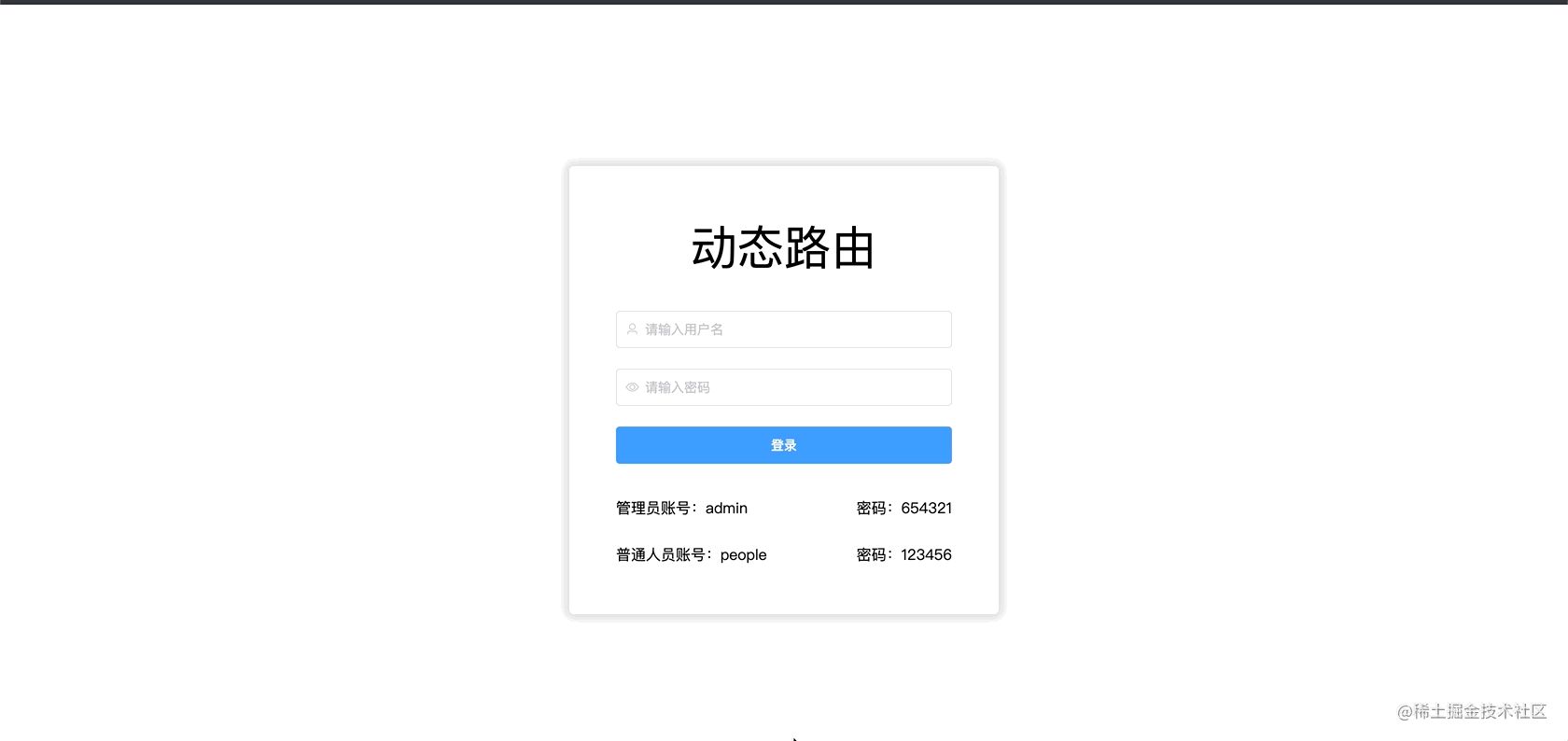
1. 技术栈说明
vue2.6 + vue-router + vuex + element-ui
2. 开始:新建项目
前提条件:在个人电脑上安装好nodejs(我的是14.15.1)之后,利用nodejs自带的npm包管理器安装好vue(我的是@vue/cli 4.5.12)
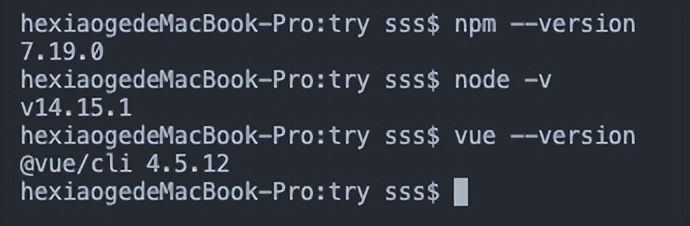
- 在命令行中通过以下指令在指定目录下安装脚手架vue-cli
npm install -g @vue/cli- 使用vue的创建项目命令,vue create xxx (xxx是指项目名称)
- 选择项目所需要的插件
? Check the features needed for your project: ? Choose Vue version // 选择vue版本 ? Babel // 支持babel ? TypeScript // 支持使用 TypeScript 书写源码 ? Progressive Web App (PWA) Support // PWA 支持 ? Router // 支持 vue-router ? Vuex // 支持 vuex ? CSS Pre-processors // 支持 CSS 预处理器。 ? Linter / Formatter // 支持代码风格检查和格式化。 ? Unit Testing // 支持单元测试。 ? E2E Testing // 支持 E2E 测试。 // 注意:你要集成什么就选就行了(注:空格键是选中与取消,A键是全选)- 选择vue的版本,由于vue3目前只出来了8个月左右,受众面不广,所以选择vue 2.x版本
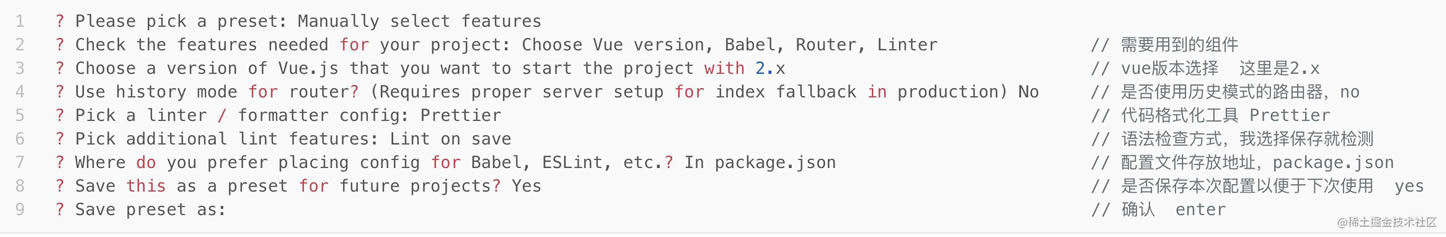
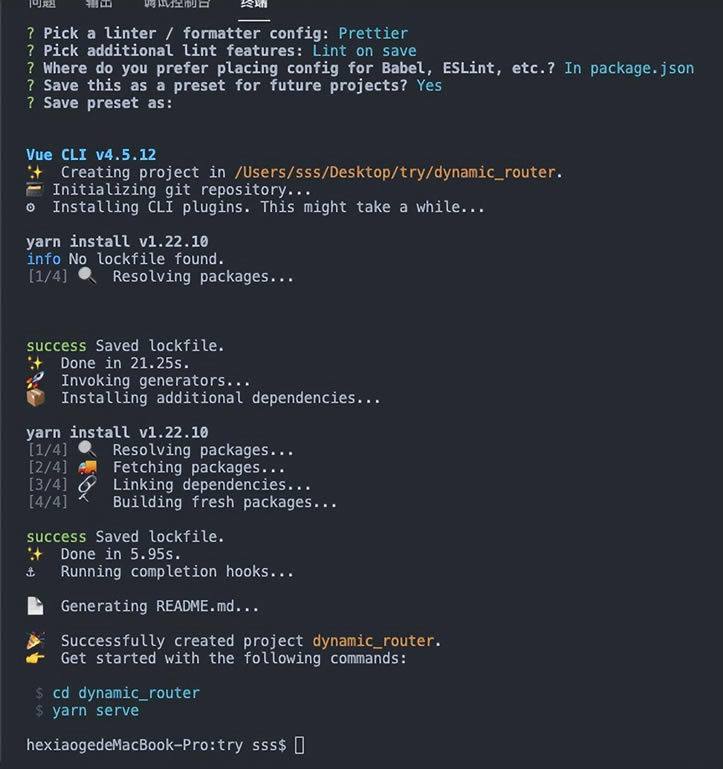
至此,项目搭建完成,可以cd打开项目,run起来了。
3. 添加element-ui以及nprogress和normalize.css和配置vue.config.js
- 先安装element-ui,nprogress和normalize.css
npm install element-ui nprogress normalize.css由于element-ui使用到了sass-loader,所以这里也是需要安装的
npm install sass-loader当前项目插件如下:

- 配置vue.config.js
vue.config.js 是一个可选的配置文件,如果项目的 (和 package.json 同级的) 根目录中存在这个文件,那么它会被 @vue/cli-service 自动加载。你也可以使用 package.json 中的 vue 字段,但是注意这种写法需要你严格遵照 JSON 的格式来写。
在根目录中创建 vue.config.js
官方配置vue.config.js的具体详解
'use strict' const path = require('path') function resolve(dir) { return path.join(__dirname, dir) } // All configuration item explanations can be find in https://cli.vuejs.org/config/ module.exports = { publicPath: '/', // 部署应用包时的基本 URL,用法和 webpack 本身的 output.publicPath 一致 outputDir: 'dist', // 构建输出目录(打包位置) assetsDir: 'static', // 放置生成的静态资源(js,css,img,fonts)的(相对于outputDir)的目录 lintOnSave: false, // 是否校验语法 productionSourceMap: false, // 如果你不需要生产环境的 source map,可以将其设置为 false 以加速生产环境构建 devServer: { port: 8888, open: true, }, configureWebpack: { // 绝对路径 resolve: { alias: { '@': resolve('src') } } } }3. 功能实现
先讲思路,让大伙有个大概的印象,不至于看代码云里雾里。
分以下几步走:
前端在本地写好路由表,以及每个路由对应的角色,也就是哪些角色可以看到这个菜单 / 路由。登录的时候,向后端请求得到登录用户的角色(管理者,普通用户)利用路由守卫者(router.beforeEach),根据取到的用户角色,跟本地的路由表进行对比,过滤出用户对应的路由,并利用路由进行菜单渲染
- 我们将储存在将storage中的token作为用户是否登录的标志,如果当前storage中有token,表明当前系统已被登录
- 将系统所有页面分为两类,需要登录才能查看的页面,不需要登录的login.vue, register.vue等
- 前端每次跳转路由时,做以下判断:

接下来从技术栈的角度补充几点:
- 在vue-router的beforeEach方法中实现以上逻辑,判断前端跳转去向;
- 出于教程考虑,不引入后端,用模拟数据的用户信息作为拦截axios发起的服务请求响应;
- 通过window.localStorage.setItem做userInfo的状态管理;
4. 实现
根据上述的步骤,我们进行每一个步骤的实现
1. 写好mock数据,用以模拟后端返回的数据源
dynamicUser里面就是模拟的后端数据,一般的后台数据库里面,就是分为一个user用户表,一个role权限路由表,这里不涉及后端,所以只给出最后后端输出的数据源。
一个完整的后端数据示例如下:
const dynamicUser = [ { name: "管理员", avatar: "https://p3.toutiaoimg.com/img/user-avatar/ccb565eca95535ab2caac9f6129b8b7a~300x300.image", desc: "管理员 - admin", username: "admin", password: "654321", token: "rtVrM4PhiFK8PNopqWuSjsc1n02oKc3f", routes: [ { id: 1, name: "/", path: "/", component: "Layout", redirect: "/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "index", path: "/index", meta: { title: "index" }, component: "index/index" }, ]}, { id: 2, name: "/form", path: "/form", component: "Layout", redirect: "/form/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/form/index", path: "/form/index", meta: { title: "form" }, component: "form/index" } ]}, { id: 3, name: "/example", path: "/example", component: "Layout", redirect: "/example/tree", meta: { title: "example" }, hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/tree", path: "/example/tree", meta: { title: "tree" }, component: "tree/index" }, { name: "/copy", path: "/example/copy", meta: { title: "copy" }, component: "tree/copy" } ] }, { id: 4, name: "/table", path: "/table", component: "Layout", redirect: "/table/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/table/index", path: "/table/index", meta: { title: "table" }, component: "table/index" } ] }, { id: 5, name: "/admin", path: "/admin", component: "Layout", redirect: "/admin/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/admin/index", path: "/admin/index", meta: { title: "admin" }, component: "admin/index" } ] }, { id: 6, name: "/people", path: "/people", component: "Layout", redirect: "/people/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/people/index", path: "/people/index", meta: { title: "people" }, component: "people/index" } ] } ] }, { name: "普通用户", avatar: "https://p3.toutiaoimg.com/img/user-avatar/6364348965908f03e6a2dd188816e927~300x300.image", desc: "普通用户 - people", username: "people", password: "123456", token: "4es8eyDwznXrCX3b3439EmTFnIkrBYWh", routes: [ { id: 1, name: "/", path: "/", component: "Layout", redirect: "/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "index", path: "/index", meta: { title: "index" }, component: "index/index" }, ]}, { id: 2, name: "/form", path: "/form", component: "Layout", redirect: "/form/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/form/index", path: "/form/index", meta: { title: "form" }, component: "form/index" } ]}, { id: 3, name: "/example", path: "/example", component: "Layout", redirect: "/example/tree", meta: { title: "example" }, hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/tree", path: "/example/tree", meta: { title: "tree" }, component: "tree/index" }, { name: "/copy", path: "/example/copy", meta: { title: "copy" }, component: "tree/copy" } ] }, { id: 4, name: "/table", path: "/table", component: "Layout", redirect: "/table/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/table/index", path: "/table/index", meta: { title: "table" }, component: "table/index" } ] }, { id: 6, name: "/people", path: "/people", component: "Layout", redirect: "/people/index", hidden: false, children: [ { name: "/people/index", path: "/people/index", meta: { title: "people" }, component: "people/index" } ] } ] } ] export default dynamicUser由此可以看出,一般登录后,返回的数据里,包含了一个用户的姓名,头像,简述以及token(username和password只是用以模拟登录用到的数据,在正常业务流中,后端不可能带出来的。),routes就是admin管理员和people普通用户的差异化动态路由了,admin多了一个admin的页面,而people是没有的。
其实这里是有多种思路的
有些开发者喜欢完整的静态路由都在前端里面,然后根据router的meta属性,写上对应user的role,登录的时候,再根据后端返回的权限,去过滤比对权限,把该用户角色所对应的路由处理好,渲染处理,这也是主流的一种处理方式。这种就等于是把所有的路由和权限业务处理都放在了前端,一旦上线发布后,想要修改就需要重新打包处理,而且不能经由后台动态新增删除例如:
//代码位置:router/index.js { path: '', component: layout, //整体页面的布局(包含左侧菜单跟主内容区域) children: [{ path: 'main', component: main, meta: { title: '首页', //菜单名称 roles: ['user', 'admin'], //当前菜单哪些角色可以看到 } }] }还有一种解法,就是所有的路由权限等,都交给后端,后端根据前端的账号密码,去获取角色权限,处理路由,丢出就是已经匹配对应角色的路由了。这种写法前端运算量不会太大,而且易于修改和后期维护以及动态的增删改查,本文就是以该种形式实现。
2. 模拟用户登录,获取用户的权限和路由
- 在main.js里面,引入该页面,用于做路由守卫者
import Vue from "vue" import App from "./App.vue" import router from "./router" import store from "./store" import ElementUI from "element-ui" import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css' import "./router/router-config" // 路由守卫,做动态路由的地方 Vue.config.productionTip = false Vue.use(ElementUI) new Vue({ router, store, render: (h) => h(App), }).$mount("#app")- 登录
本来我是写了mock数据,模拟用户登录,请求后端角色的接口,奈何mock挂了,
所以我就直接模拟了:取到用户角色,存放进localStorage,然后跳转主页
- 在这里,由于用了element-ui的form表单提交,所以直接this.$refs.userForm.validate
element-ui的form表单提交文档!
- 这里的dynamicUser是mock的数据流,一般后端是直接直接返回对应的结果,可由于fastmock容易挂掉,所以就直接手写mock了。
定义flag用于做登录校验,如果循环都找不到对应的username和password的话,就告诉用户,该账号密码错误,登录失败..可如果有一次是成功的,那么flag就是为!0的,并且返回对应的用户信息,用户路由等。。最后还会进行路由的跳转初始化页面(首页),并进行动态路由加载和路由跳转。
import dynamicUser from "../../mock" import { Message } from "element-ui" login() { this.$refs.userForm.validate(( valid ) => { if(valid) { let flag = !1 window.localStorage.removeItem("userInfo") dynamicUser.forEach(item => { if(item["username"] == this.user['username'] && item["password"] == this.user['password']) { flag = !0 Message({ type: 'success', message: "登录成功", showClose: true, duration: 3000 }) window.localStorage.setItem("userInfo", JSON.stringify(item)) // 这里用catch捕获错误,而且不打印,解释在下方 this.$router.replace({ path: "/" }).catch(() => {}) } }) if(!flag) Message({ type: 'warning', message: "账号密码错误,请重试!", showClose: true, duration: 3000 }) } else return false }) }
解释:如果不捕获catch错误,而且不打印的话,就会出现如图所示的错误。
原因:vue-router路由版本更新产生的问题,导致路由跳转失败抛出该错误,但并不影响程序功能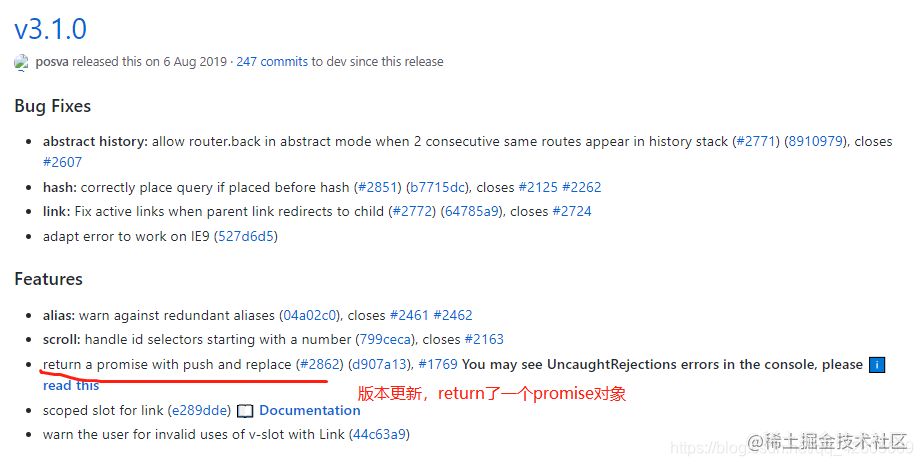
- 解决方案1:
在使用编程式导航跳转时,每次使用,后面都跟上.catch方法,捕获错误信息this.$router.push("/xxx").catch(() => {})
- 解决方法2:
全局解决,替换路由的Push和replace方法,放在src/router/index.js中:
const originalPush = VueRouter.prototype.push VueRouter.prototype.push = function push(location, onResolve, onReject) { if (onResolve关键词:vue完成用户登录验证(vue完成登录注册与验证码)